Characteristics
Larix decidua can reach a height of up to 35 meters. The trunk diameter can be up to 60 centimeters. The European larch is a deep-rooted species with extensive roots. The crown is usually narrow and therefore conical. The wood is rich in resin, tough and extremely elastic. Larix decidua has the hardest and most durable wood of our conifers.
Pollination as well as needlework
Larix decidua is monoecious. Pollination takes place here by the wind. Male flowers have a yellowish, female, however, a reddish color. The needles are 10-30 millimeters long and have a light green color. In autumn, however, it turns yellow to golden yellow. The cones are 2-3 centimeters tall. They have an oval to spherical shape.
Soil condition
Larix decidua prefers a sunny and nutrient-rich location. The recommended soil quality can be defined as fresh to moist. The optimal soil for the European larch should also have a rich supply of nutrients with a deep depth. Low humidity is no problem for Larix decidua. It also thrives on calcareous soils.
Provenance
The common name of this conifer points to the old continent as the original distribution area. Larix decidua can be found in the Alps at an altitude of up to 2500 meters. We have several origins in our range and can easily supply you with your desired provenance.
Uses
The wood of the Larix decidua is very versatile. In the wood industry people enjoy the possible uses as construction wood as well as furniture wood. In forest science, people are happy about the diverse forest ecological skills. The European larch can be used in combination with the common beech as basic equipment for a sustainable forest ecosystem. We would be happy to advise you on planning your forest ecosystem.
Please enter your wishes of origin in the comment field.
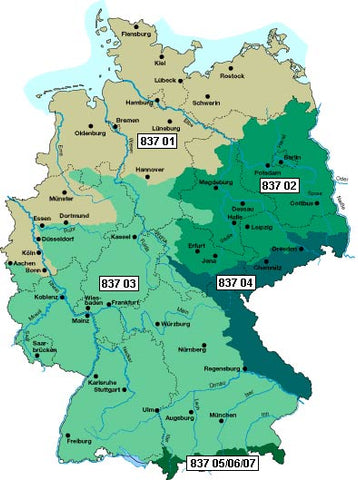
Origin table
| 837 01 | North German Lowlands |
| 837 02 | Middle and East German Low and hill country |
| 837 03 | West and South German Hills and mountains |
| 837 04 | Southeast German Hill and mountainous country |
| 837 05 | Alps, submontane level |
| 837 06 | Alps, montane level |
| 837 07 | Alps, subalpine level |




